Introduction to Python
Python Overview
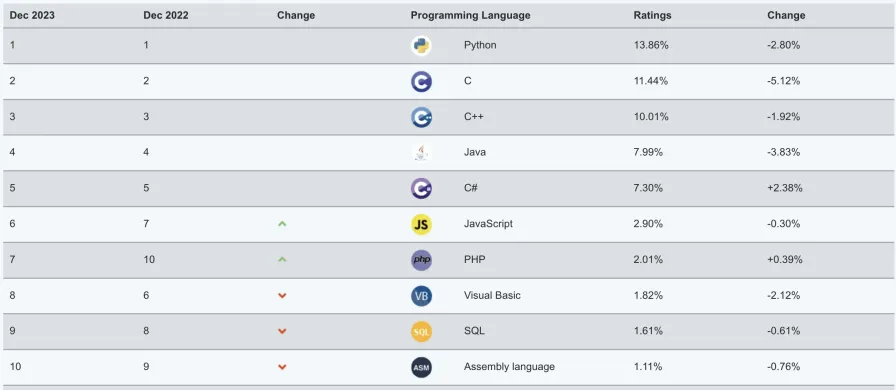
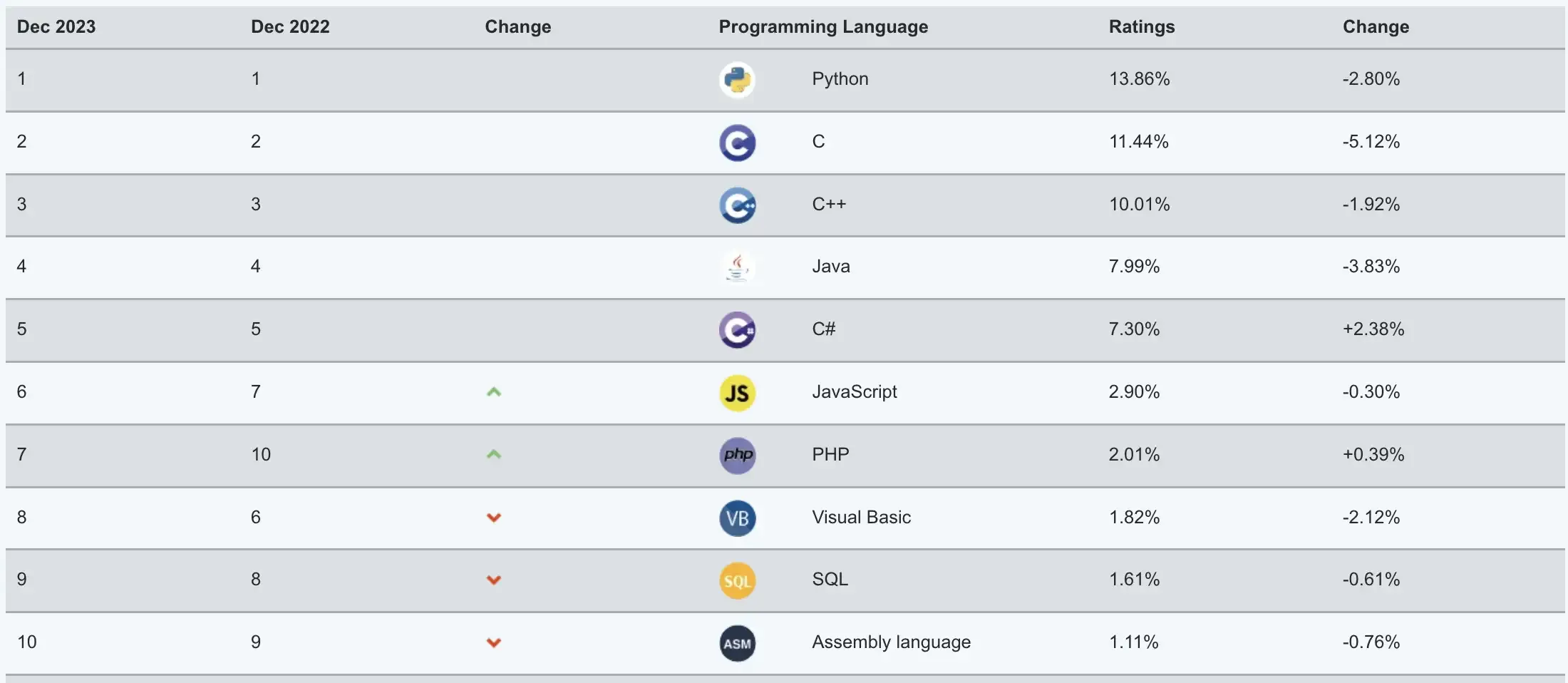
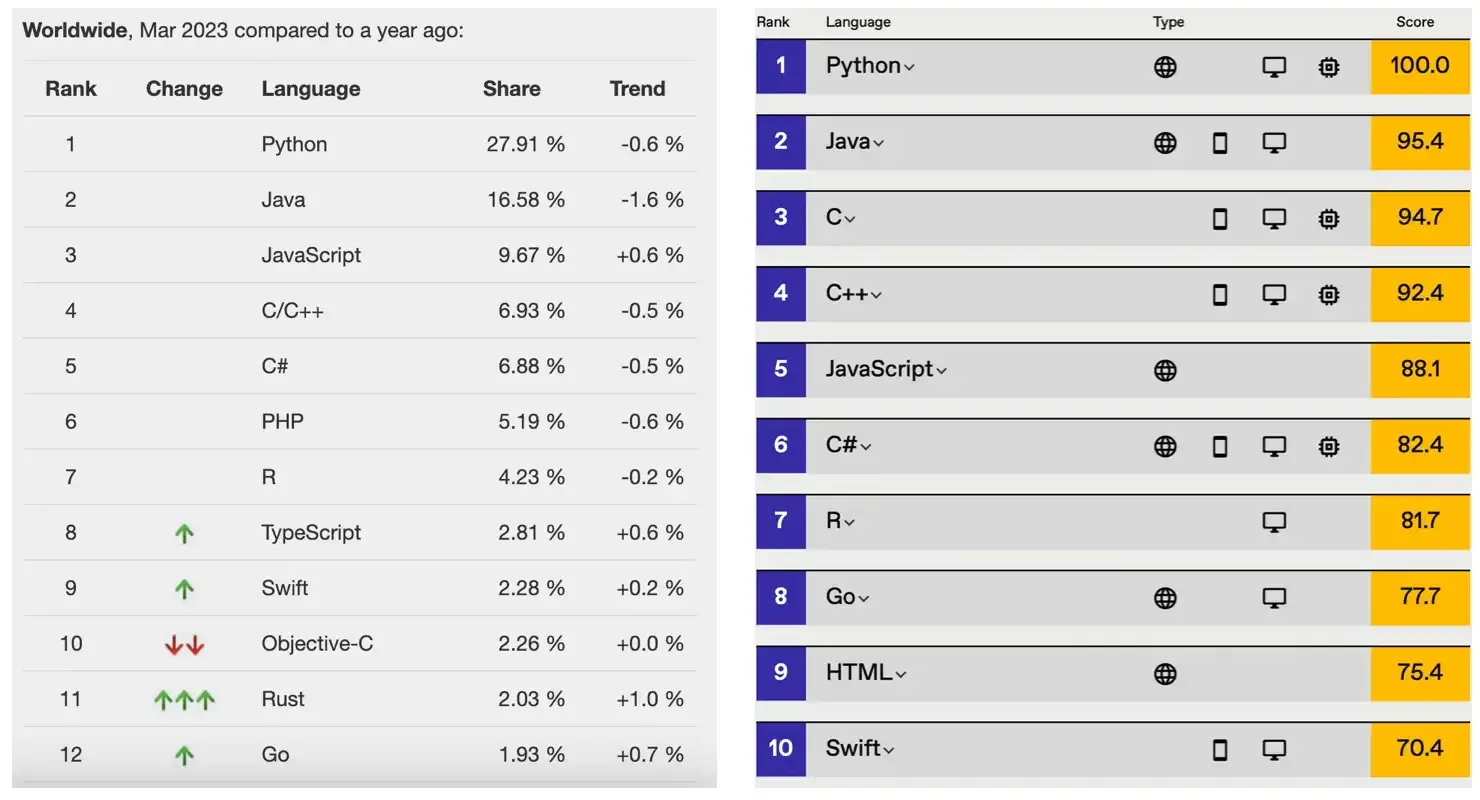
Python (British pronunciation: /ˈpaɪθən/; American pronunciation: /ˈpaɪθɑːn/) is a programming language invented by Dutch programmer Guido van Rossum. It is currently one of the most popular programming languages in the world with the largest user base. Python emphasizes code readability and syntax simplicity. Compared to equally influential programming languages like C, C++, and Java, Python allows users to express their intentions with less code. Below are Python’s rankings from several authoritative programming language indices. The first image is provided by TIOBE Index, and the third image is provided by IEEE Spectrum. The second image is particularly noteworthy as it shows the popularity of programming languages on GitHub, the world’s largest code hosting platform, where Python has held the top position for the past four years.
Python Timeline
Here are some important milestones in Python’s development:
- December 1989: Guido van Rossum decided to develop a new scripting language and its interpreter to pass the boring Christmas holiday. The new language would be a successor to ABC language, primarily used to replace Unix shell and C language for system administration. Since Guido was a devoted fan of the BBC TV series “Monty Python’s Flying Circus”, he chose the word Python as the name for the new language.
- February 1991: Guido van Rossum released the initial code of the Python interpreter on the alt.sources newsgroup, marked as version 0.9.0.
- January 1994: Python 1.0 was released, where the dream began.
- October 2000: Python 2.0 was released, making the entire development process more transparent and gradually forming an ecosystem.
- December 2008: Python 3.0 was released, introducing many new features of modern programming languages, but not fully backward compatible.
- April 2011: pip was first released, giving Python its own package management tool.
- July 2018: Guido van Rossum announced his “permanent vacation” from the position of “Benevolent Dictator For Life” (the person with final decision-making authority when disputes arise in open-source project communities).
- January 2020: After 11 years of Python 2 and Python 3 coexistence, official support for Python 2 updates and maintenance was discontinued, encouraging users to switch to Python 3 as soon as possible.
- Present: Python is widely used in large language models (GPT-3, GPT-4, BERT, etc.), computer vision (image recognition, object detection, image generation, etc.), intelligent recommendation systems (YouTube, Netflix, ByteDance, etc.), autonomous driving (Waymo, Apollo, etc.), speech recognition, data science, quantitative trading, automated testing, automated operations, and many other fields. Python’s ecosystem is thriving.
Note: Most software version numbers are generally divided into three segments, in the form A.B.C, where A represents the major version number, which increases when the software is completely rewritten or upgraded with backward-incompatible changes; B represents feature updates, increasing when new features appear; C represents minor changes (e.g., fixing a bug), increasing with any modification.
Python Advantages and Disadvantages
Python has many advantages. Here are a few:
- Simple and elegant, compared to many other programming languages, Python is easier to learn.
- Can do more with less code, improving development efficiency.
- Open source with a strong community and ecosystem.
- Extremely versatile, with strong adaptability.
- Glue language, capable of binding things developed in other languages.
- Interpreted language, easier to be cross-platform, running on multiple operating systems.
Python’s main disadvantage is low execution efficiency (a common problem with interpreted languages). If code execution efficiency is more important, C, C++, or Go might be better choices.
Installing Python Environment
A craftsman must sharpen his tools before doing good work. To start your Python programming journey, you first need to install the Python environment on your computer, which simply means installing the Python interpreter needed to run Python programs. We recommend installing the official Python 3 interpreter, which is written in C and commonly referred to as CPython. It’s probably your best choice right now. First, we need to find the download link from the official website’s download page. Click the “Download” button to enter the download page, then select the appropriate Python 3 installer based on your operating system, as shown below.
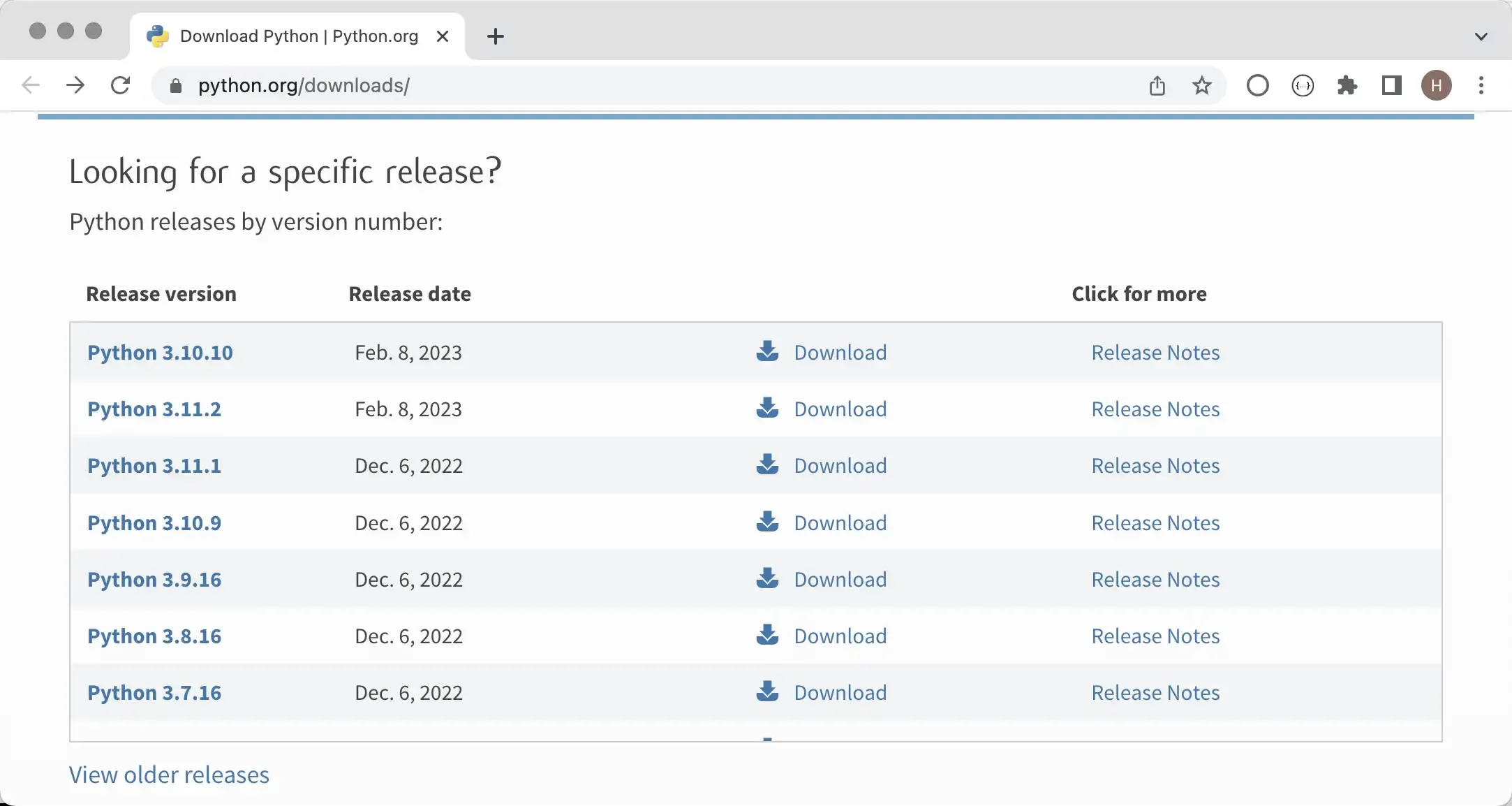
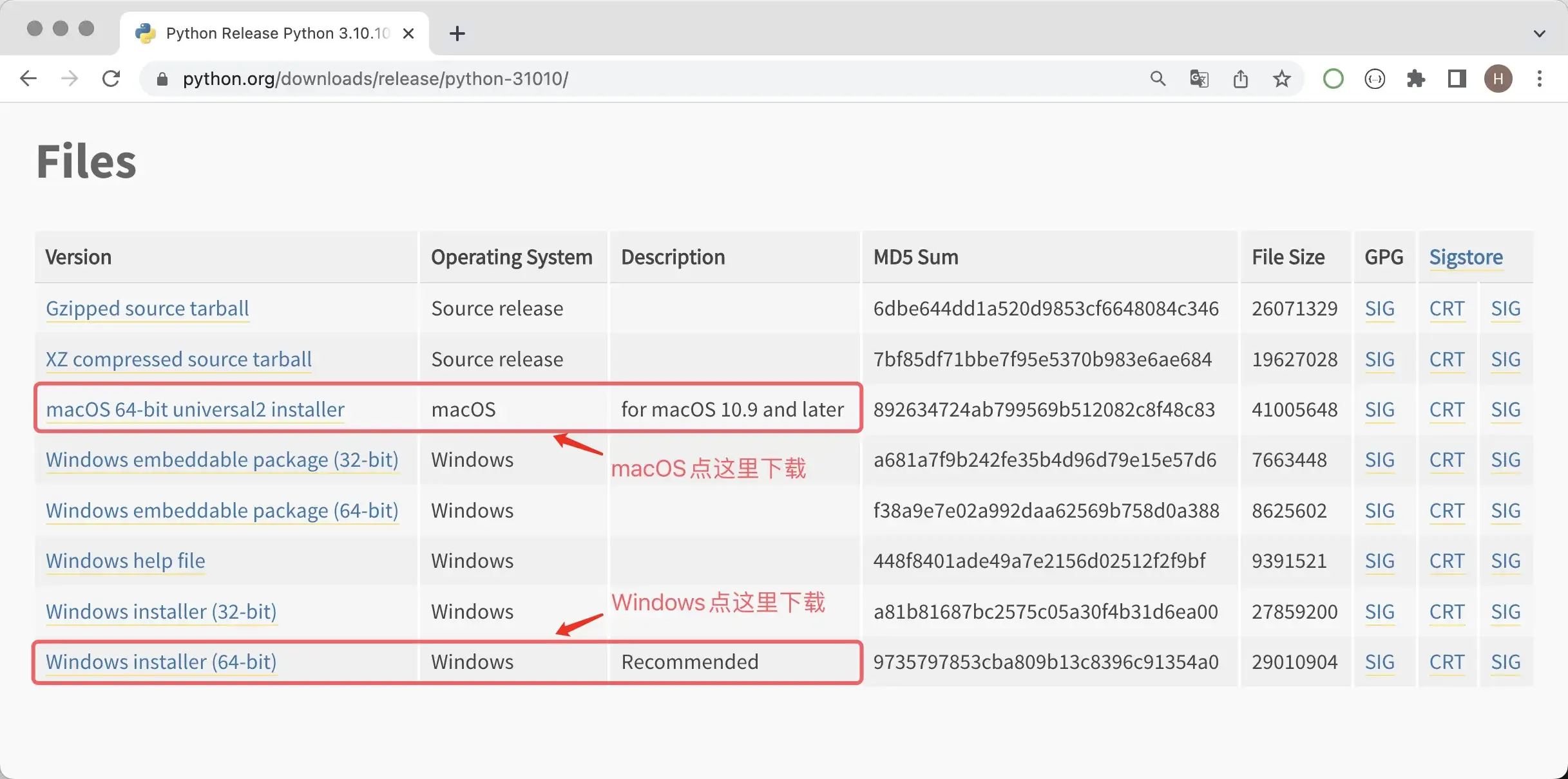
After entering the download page, some Python versions don’t provide installers for Windows and macOS systems, only compressed source code files. For those familiar with Linux systems, we can build and install from source code. For those using Windows or macOS systems, we strongly recommend using the installer. For example, if you want to install Python 3.10, choosing Python 3.10.10 or Python 3.10.11 will provide Windows or macOS installation packages, while other versions may only have source code, as shown below.
Windows Environment
Below we’ll use Windows 11 as an example to explain how to install the Python environment on Windows operating systems. Double-click the installer downloaded from the official website to open the installation wizard, as shown below.
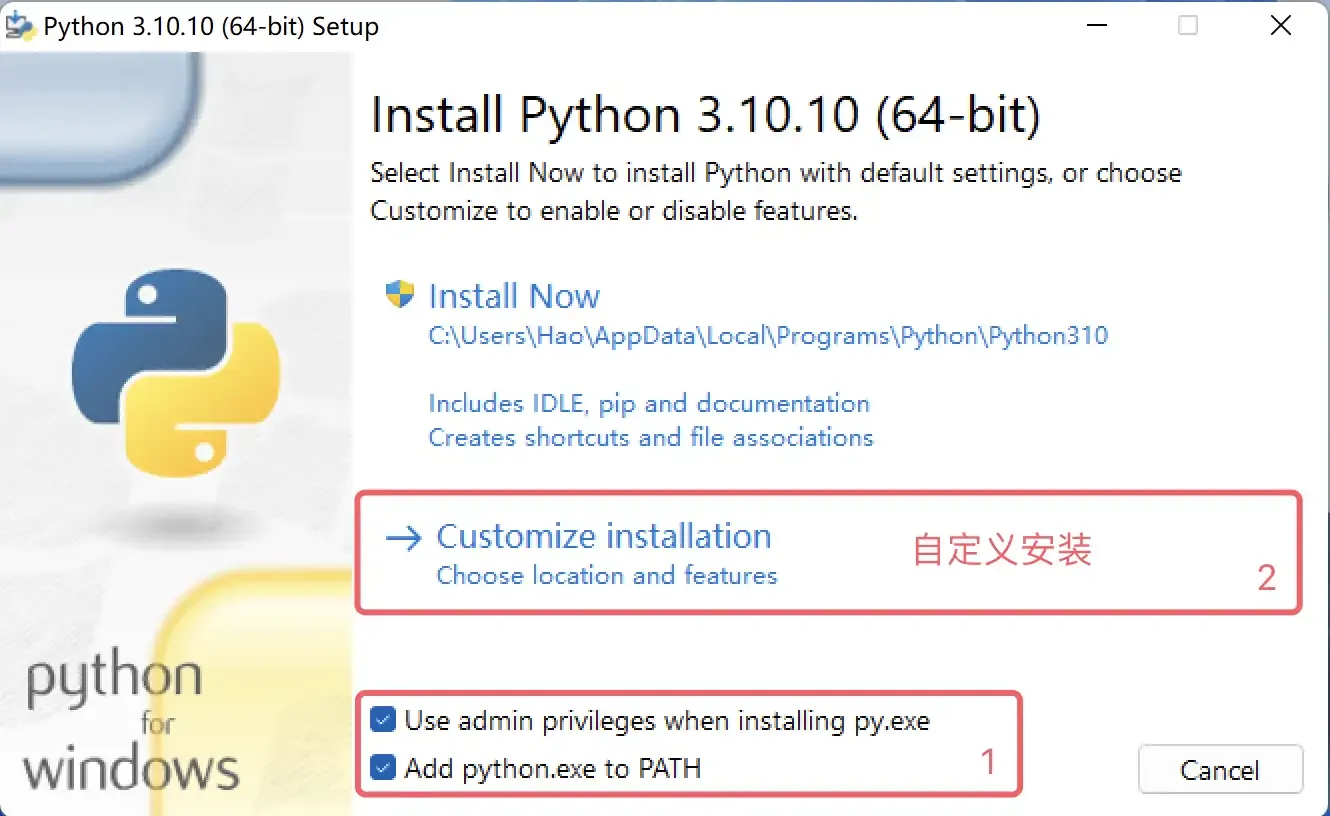
First, be sure to check the “Add python.exe to PATH” option, which will help us add the Python interpreter to the Windows system’s PATH environment variable (don’t worry if you don’t understand, just check it). Second, “Use admin privileges when installing py.exe” is to obtain administrator privileges during installation, and we recommend checking it. Then, we select “Customize Installation” to use custom installation mode, which is the choice of professionals, and you are (pretending to be) that professional. We don’t recommend using “Install Now” (default installation).
Next, the installation wizard will prompt you to check the required “Optional Features”. Here we can select all of them. The second item is worth mentioning - it’s Python’s package management tool pip, which can help us install third-party libraries and tools, so be sure to check it, then click “Next” to proceed.
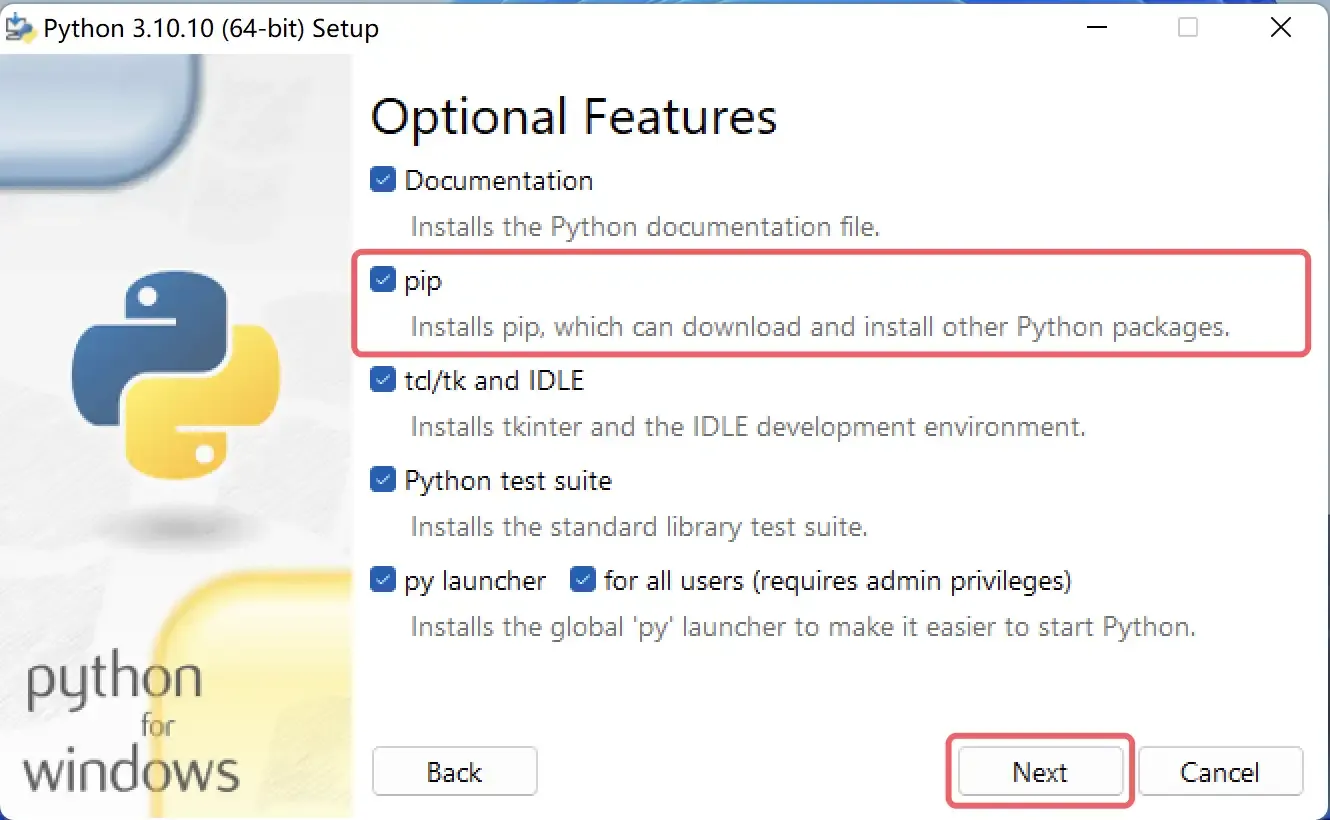
Next is the selection of “Advanced Options”. Here we recommend only checking “Add Python to environment variables” and “Precompile standard library”. The former will help us automatically configure environment variables, and the latter will precompile the standard library (generating .pyc files), so there’s no need for temporary compilation when using them. Again, don’t worry if you don’t understand, just check them. The “Customize install location” below is strongly recommended to be changed to a custom path. This path should not contain Chinese characters, spaces, or other special characters. Paying attention to this will save you a lot of unnecessary trouble in the future. After completing the settings, click “Install” to begin installation.
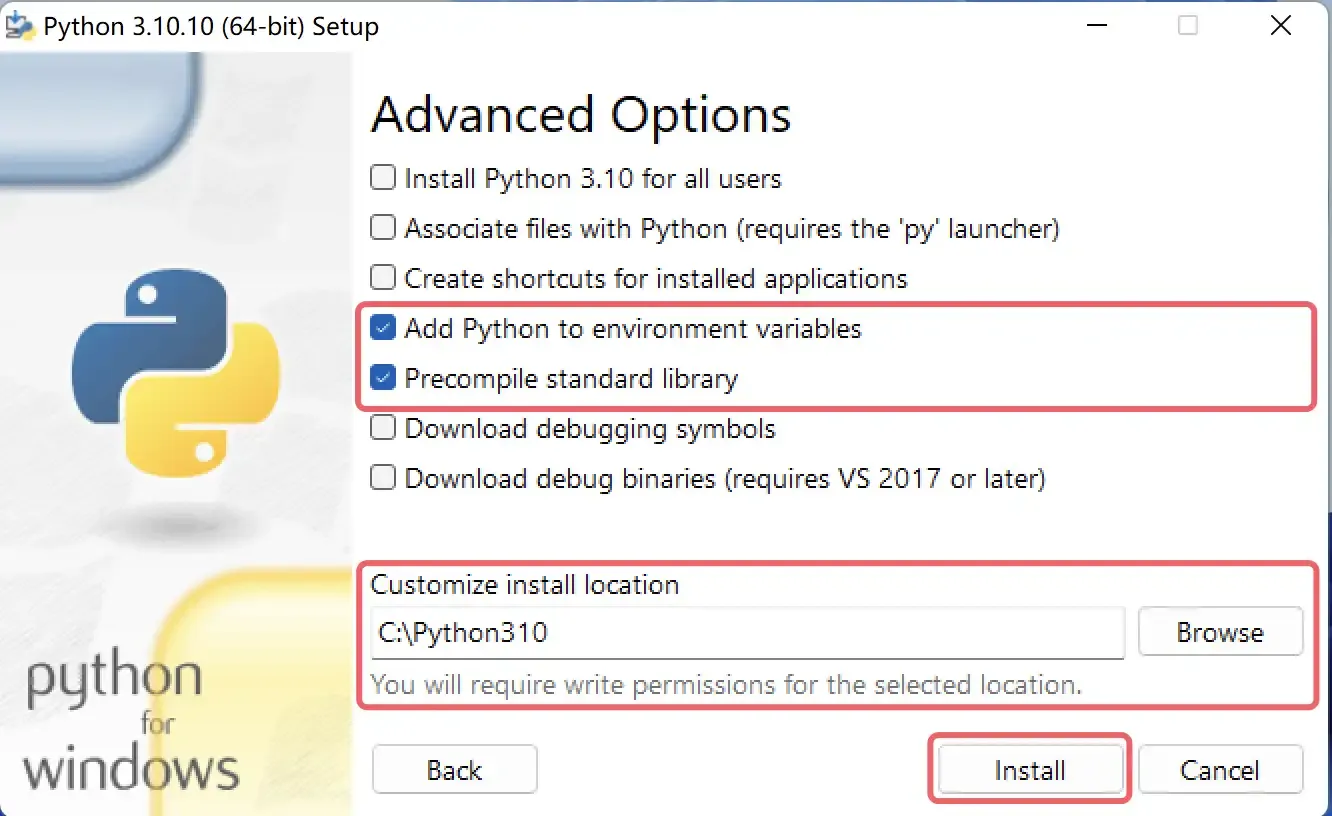
A successful installation will show the screen below. The keyword for successful installation is “successful”. If installation fails, the word here will change to “failed”.
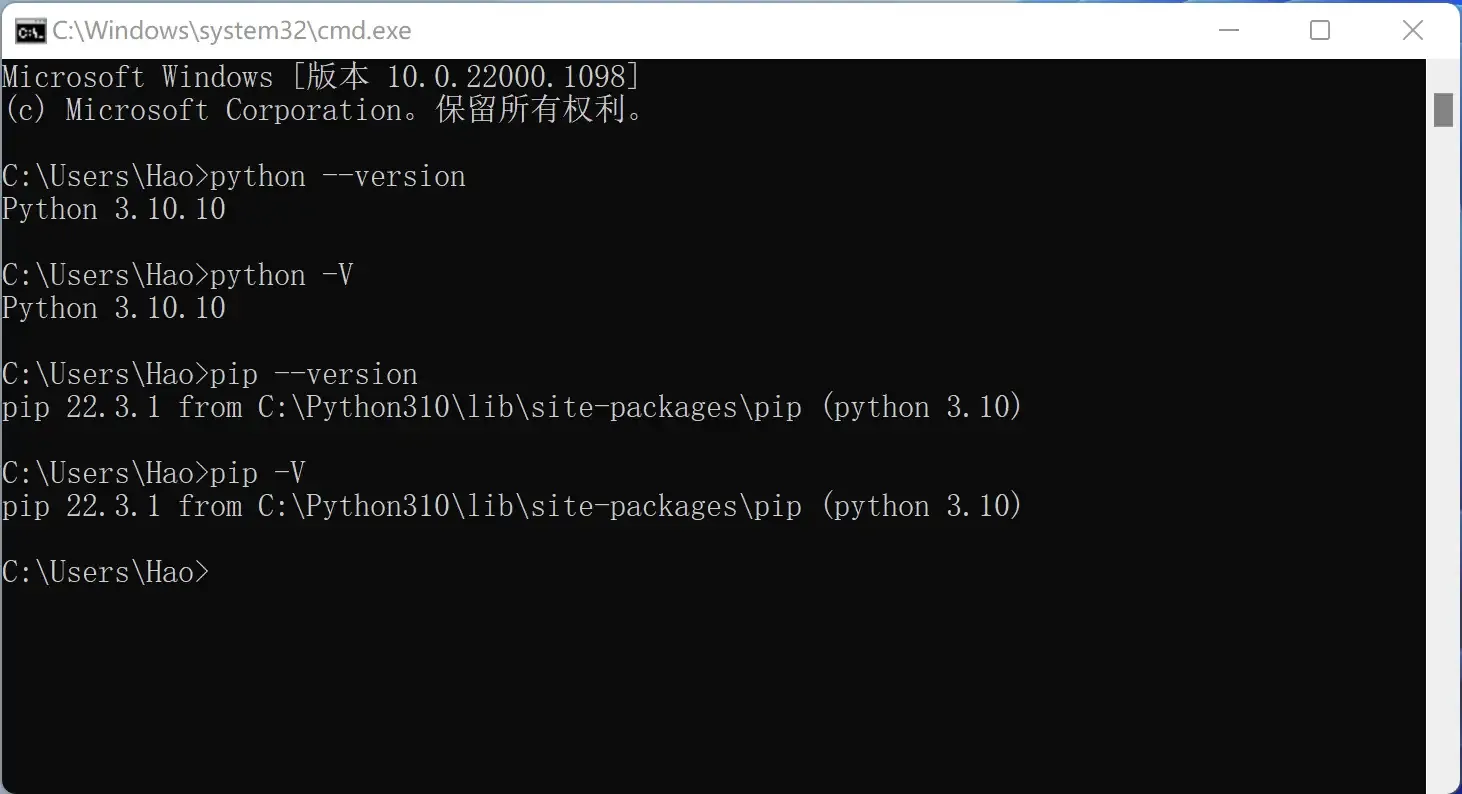
After installation, you can open Windows “Command Prompt” or PowerShell, then enter python --version or python -V to check if the installation was successful. This command checks the version number of the Python interpreter. If you see the screen shown below, congratulations, the Python environment has been successfully installed. We also recommend checking if Python’s package management tool pip is available, using the command pip --version or pip -V.
Note: If the installation process reports errors or indicates installation failure, it’s likely that your Windows system is missing some dynamic link library files or necessary build tools. You can download “Visual Studio 2022 Build Tools” from Microsoft’s official website for repair, as shown below. If it’s inconvenient to download from Microsoft’s official website, you can also use the following Baidu Cloud link to obtain the repair tool. Link: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1iNDnU5UVdDX5sKFqsiDg5Q Extraction code: cjs3.
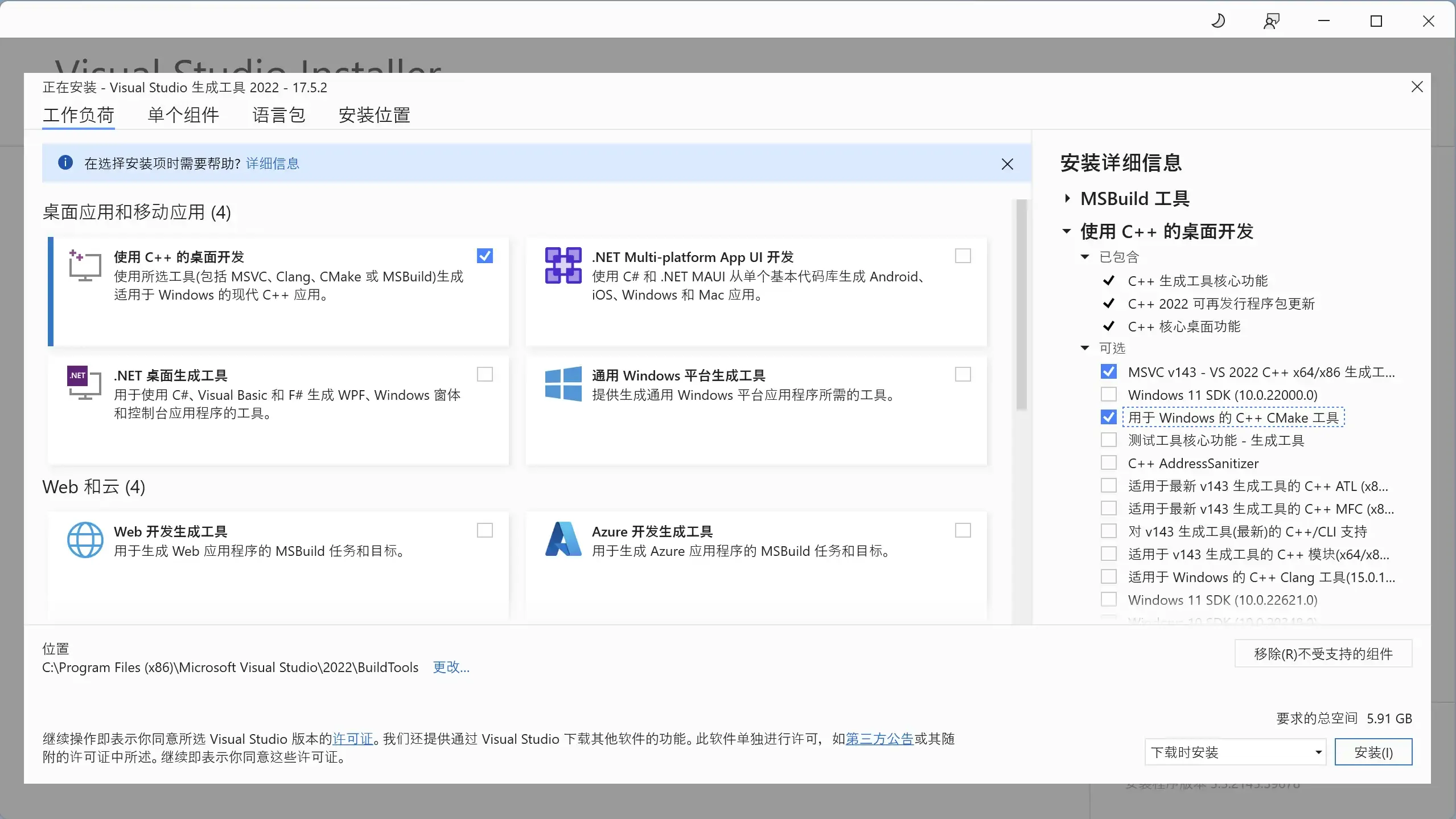
The “Visual Studio 2022 Build Tools” downloaded above requires an internet connection to run. After running, the screen shown below will appear. You can refer to the image below to check the corresponding options for repair. The repair process requires downloading corresponding software packages online, which may take some time. After successful repair, you may be asked to restart your operating system.
macOS Environment
Installing the Python environment on macOS is simpler than on Windows. The installation package we download from the official website is a pkg file. After double-clicking to run it, just keep clicking “Continue” and the installation will be successful, with almost no settings or selections needed, as shown below.
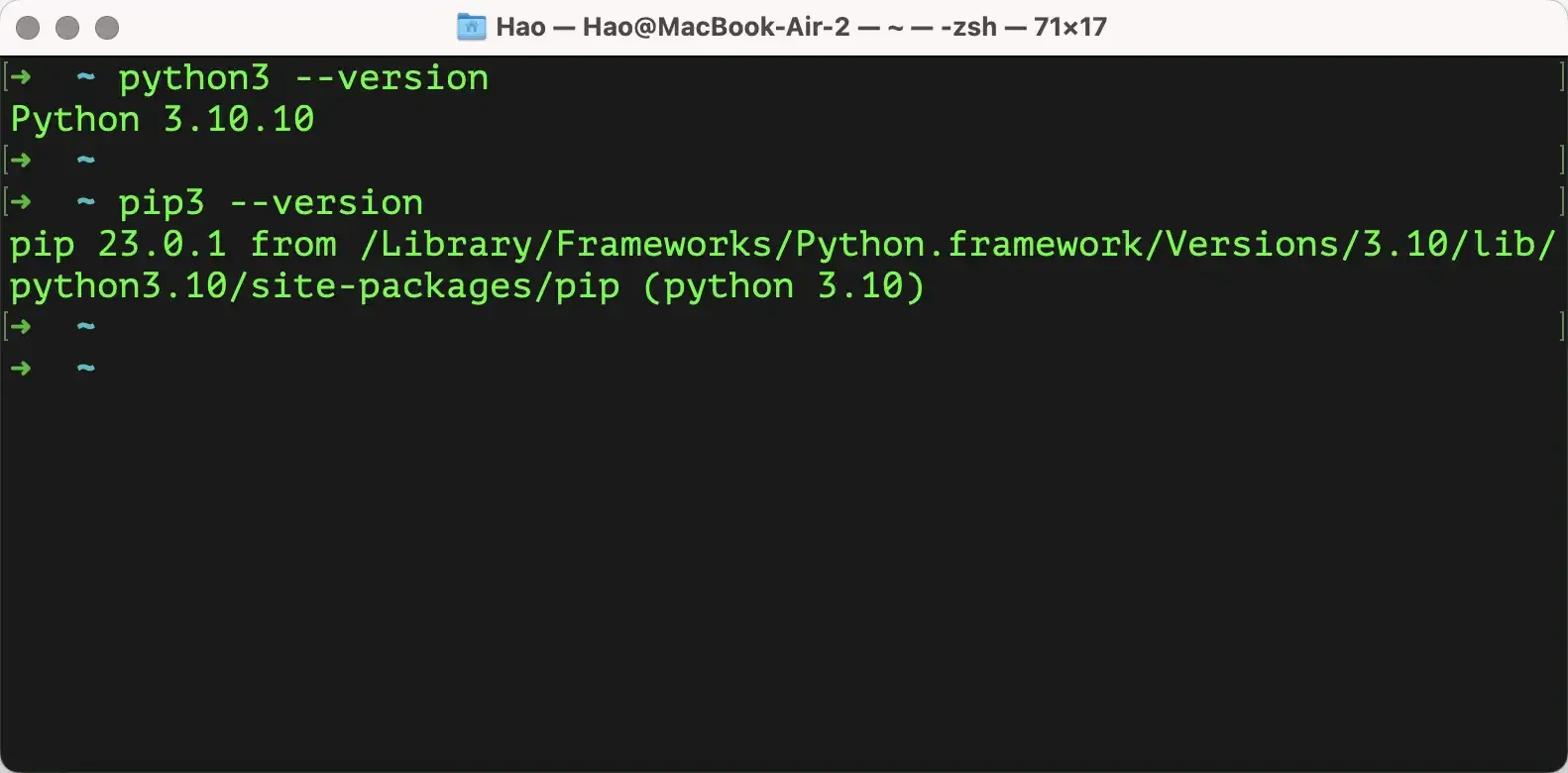
After installation, you can enter the command python3 --version in macOS’s “Terminal” tool to check if the installation was successful. Note that the command here is python3, not python!!! Then let’s check the package management tool by entering the command pip3 --version, as shown below.
Other Installation Methods
Some people might recommend that beginners directly install Anaconda, because Anaconda will help us install the Python interpreter and some commonly used third-party libraries, and also provides some convenient tools, which is particularly suitable for newbies. I personally don’t recommend this approach because when installing Anaconda, you’ll inexplicably install a bunch of useful and useless third-party libraries (taking up a lot of disk space), and your terminal or command prompt will be hijacked by Anaconda (automatically activating the virtual environment every time it starts), which doesn’t conform to the principle of least astonishment in software design. Other minor issues with Anaconda won’t be elaborated here. If you must use Anaconda, I recommend installing Miniconda, which is on the same download page as Anaconda.
Newbies often hear or say, “I want to write Python programs, can’t I just install PyCharm?” Here’s a simple explanation: PyCharm is just a tool to assist in writing Python code. It doesn’t have the ability to run Python code itself. Running Python code relies on the Python interpreter we installed above. Of course, some PyCharm versions will prompt you to download the Python interpreter online if they don’t detect a Python environment on your computer when creating a Python project. We’ll cover PyCharm installation and usage in the next lesson.
Summary
Let’s summarize what we’ve learned:
- Python is a powerful language that can do many things, so it’s worth learning.
- To use Python, you first need to install the Python environment, which is the Python interpreter needed to run Python programs.
- On Windows systems, you can enter
python --versionin Command Prompt or PowerShell to check if the Python environment is successfully installed; on macOS systems, you can enterpython3 --versionin Terminal to check.